
FWPayload is a small RISC-V core+peripherals subsystem, targeting the user-project area of Caravel.
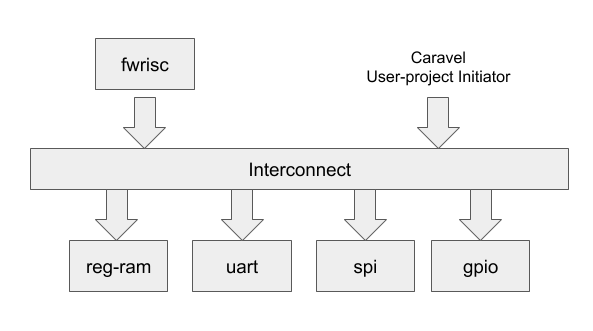
The subsystem is accessible from the management processor as a target device, and the subsystem can also be accessed and single-stepped using the logic-analyzer interface.
Tests for the subsystem are written in Python using cocotb.
FWPayload uses several pieces of external IP. Some are bundled with the project, and some are fetched during the project-initialization step.
RISC-V core originally targeted for FPGA application - Git: https://github.com/mballance/fwrisc.git - License: Apache 2.0
Parameterized Wishbone interconnect - Git: https://github.com/featherweight-ip/fw-wishbone-interconnect - License: Apache 2.0
SPI master IP, obtained from the Caravel repository. Bundled with the project. - License: GNU LGPL
UART IP, obtained from the Caravel repository. Bundled with the project. - License: BSD-style
The FWPayload memory map is designed to fit within the 28-bit user-area portion of the Caravel memory map.
0 (i) - unused 1 (i) - unused 2 (i) - unused 3 (i) - unused 4 (i) - unused 5 (i) - unused 6 (i) - unused 7 (i) - unused 8 (i) - unused 9 (i) - unused 10 (i) - unused 11 (i) - unused 12 (o) - GPIO-out [0] 13 (o) - GPIO-out [1] 14 (o) - GPIO-out [2] 15 (o) - GPIO-out [3] 16 (o) - UART Tx 17 (i) - UART Rx 18 (i) - SPI SDI 19 (o) - SPI CSB 20 (o) - SPI SCK 21 (o) - SPI SDO 22 (o) - SPI SDOENB 23 (o) - GPIO-out [4] 24 (o) - GPIO-out [5] 25 (o) - GPIO-out [6] 26 (o) - GPIO-out [7] 27 (i) - GPIO-in [0] 28 (i) - GPIO-in [1] 29 (i) - GPIO-in [2] 30 (i) - GPIO-in [3] 31 (i) - GPIO-in [4] 32 (i) - GPIO-in [5] 33 (i) - GPIO-in [6] 34 (i) - GPIO-in [7] 35 (i) - unused 36 (i) - unused 37 (i) - unused
FWPayload uses the Caravel logic analyzer to configure reset and clocking, probe the program counter of the FWRISC, and optionally, single-step the clock.
The FWPayload project uses IVPM (IP and Verification Package Manager) to manage external IP and Python dependencies. The project can be setup both with and without IVPM installed.
In both cases, setting up the project will result in creation of a packages directory within the project that contains external IPs and required Python packages.
Ensure IVPM is installed:
% pip3 install ivpm --user --upgrade
% cd <fwpayload_dir>
% ivpm update
The project can also be setup without installing IVPM. The bootstrap.sh script is provided for this purpose. bootstrap.sh clones a local copy of ivpm.
% cd <fwpayload_dir>
% ./bootstrap.sh
Testing of the fwpayload subsystem is done using a cocotb test environment. The block diagram is shown below:
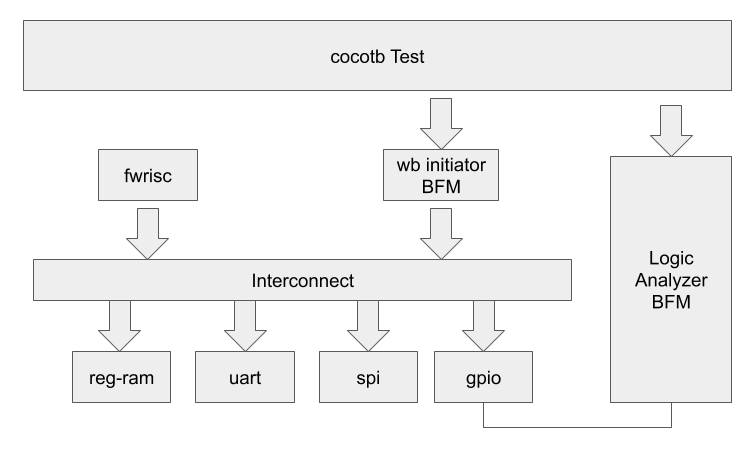
Bus Functional Models (BFMs) are used to drive the Caravel management interface and logic-analyzer pins.
Drives the clock via the logic-analzer interface while monitoring the GPIO outputs
mgmt_mem_access
Individual tests are run from the dv/ directory by running 'make'.
% cd dv/fwrisc_gpio
% make clean
% make
Test behavior is controlled using environment variables. - SIM - Selects the simulator to run - icarus -- Icarus Verilog (default) - vlsim -- Verilator, via the vlsim front-end - DEBUG[=1] - Controls whether wave files should be saved
A Johnson counter is a modified ring counter in which the output from the last flip flop is inverted and fed back as an input to the first. It is also called as Inverse Feedback COunter or Twisted Ring Counter. It is used in hardware logic design to create complicated Finite States Machine (FSM) eg: ASIC and FPGA design. It roughly consumes 80-100 mW of power and runs at a clock frequency of 36 MHz.
1.00
sky130A